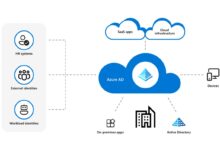
Ever wondered how top companies deploy apps at lightning speed? The answer often lies in Azure apps—Microsoft’s powerhouse for cloud innovation, scalability, and seamless integration.
What Are Azure Apps and Why They Matter

Azure apps refer to a broad range of application services offered by Microsoft Azure, enabling developers and enterprises to build, deploy, and manage applications through cloud infrastructure. These services are not just about hosting; they’re about transforming how software is developed, delivered, and scaled in modern IT environments.
Defining Azure Apps in the Cloud Ecosystem
Azure apps encompass multiple services such as Azure App Service, Azure Functions, Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and more. These tools allow developers to run web apps, mobile backends, APIs, and serverless functions without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Azure App Service: Ideal for web and mobile app hosting with built-in CI/CD.
- Azure Functions: Enables event-driven, serverless computing.
- Azure Logic Apps: Automates workflows across cloud and on-premises systems.
These services are interconnected, forming a cohesive platform for end-to-end application development. For example, a mobile app backend can be hosted on Azure App Service, triggered by events via Azure Functions, and integrated with third-party SaaS tools using Logic Apps.
“Azure isn’t just a cloud platform—it’s a complete application ecosystem.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
Evolution of Azure Apps Over the Years
Since its launch in 2010, Azure has evolved from a simple PaaS offering into a full-fledged cloud suite. Azure apps have grown alongside this transformation. Initially focused on .NET web apps, Azure App Service now supports Python, Node.js, Java, PHP, and Docker containers.
The introduction of serverless computing with Azure Functions in 2016 marked a pivotal shift. It allowed developers to run code in response to events without provisioning servers—reducing cost and complexity. Similarly, Azure Static Web Apps, launched in 2020, brought Jamstack architecture to the mainstream, enabling fast, secure frontend deployments with backend APIs.
This evolution reflects Microsoft’s commitment to developer experience and hybrid cloud flexibility. Today, Azure apps support multi-cloud strategies, on-premises integration via Azure Arc, and edge computing with Azure IoT Edge.
Core Components of Azure Apps Ecosystem
The strength of Azure apps lies in its modular, service-oriented architecture. Each component serves a specific purpose but integrates seamlessly with others, creating a powerful development environment.
Azure App Service: The Backbone of Web Applications
Azure App Service is the most widely used service under the Azure apps umbrella. It allows you to host web apps, REST APIs, and mobile backends with automatic scaling, SSL support, and deployment slots for staging environments.
- Supports multiple languages and frameworks.
- Offers built-in DevOps integration with GitHub, Azure DevOps, and Bitbucket.
- Enables zero-downtime deployments using deployment slots.
One of the standout features is its integration with Azure Active Directory (AAD) for secure authentication. You can also use custom domains and automated backups, making it ideal for enterprise-grade applications.
Learn more about Azure App Service on Microsoft’s official documentation.
Azure Functions: Serverless Computing Made Simple
Azure Functions brings the power of serverless computing to Azure apps. Instead of managing servers or VMs, developers write small pieces of code (functions) that run in response to triggers like HTTP requests, timer events, or messages from queues.
- Pay-per-execution pricing model reduces costs.
- Supports C#, JavaScript, Python, Java, and PowerShell.
- Integrates with Azure Event Grid, Service Bus, and Cosmos DB.
For instance, an image upload to Azure Blob Storage can automatically trigger a function to resize the image and store the thumbnail—without any server management.
This model is perfect for microservices, background processing, and event-driven architectures. It’s also a key enabler for DevOps automation and real-time data processing.
Azure Logic Apps: Workflow Automation at Scale
While Azure Functions handle code execution, Azure Logic Apps manage workflow orchestration. These are visual tools that let you automate business processes by connecting various services—both cloud and on-premises.
- Drag-and-drop designer for building workflows.
- Pre-built connectors for Salesforce, Office 365, SQL Server, and more.
- Supports enterprise integration patterns like EDI and B2B messaging.
A retail company might use Logic Apps to automate order processing: when a new order arrives in Dynamics 365, it triggers a workflow that checks inventory in SQL Database, sends a confirmation email via SendGrid, and updates the shipping system.
Logic Apps complement Azure apps by reducing the need for custom coding in integration scenarios, accelerating development cycles.
Benefits of Using Azure Apps for Modern Development
Organizations choose Azure apps not just for functionality but for strategic advantages in speed, cost, and reliability.
Scalability and Performance Optimization
One of the biggest advantages of Azure apps is automatic scalability. Whether you’re running a small startup website or a global e-commerce platform, Azure can scale resources up or down based on traffic.
- Auto-scaling rules based on CPU, memory, or request metrics.
- Integration with Azure Monitor for real-time performance tracking.
- Global distribution via Azure CDN and Traffic Manager.
For example, during a product launch, an app hosted on Azure App Service can scale from 2 instances to 20 within minutes, then scale back down when traffic normalizes—ensuring optimal performance without over-provisioning.
“With Azure, we scaled our user base from 10K to 1M in six months without a single outage.” — Tech Startup CTO
Cost Efficiency and Pay-as-You-Go Model
Azure apps follow a consumption-based pricing model. You only pay for what you use, which is especially beneficial for startups and variable workloads.
- Azure Functions charge per million executions and execution time.
- Azure App Service offers free and shared tiers for testing.
- Reserved instances and hybrid benefits reduce long-term costs.
Additionally, Azure Hybrid Benefit allows organizations with existing Windows Server or SQL Server licenses to apply them in the cloud, saving up to 40% on virtual machines and databases.
This flexibility makes Azure apps accessible to businesses of all sizes, eliminating the need for large upfront investments in hardware.
Security and Compliance Features
Security is baked into every layer of Azure apps. Microsoft invests over $1 billion annually in cybersecurity and operates one of the most secure cloud infrastructures globally.
- Network security groups (NSGs) and Azure Firewall protect app endpoints.
- Integration with Azure Active Directory for identity management.
- Compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and SOC 2.
Azure Key Vault securely stores secrets, certificates, and encryption keys, preventing hardcoded credentials in apps. Additionally, Azure Security Center provides unified security management and advanced threat protection across hybrid cloud workloads.
For regulated industries like healthcare and finance, these features ensure that Azure apps meet strict compliance requirements without additional overhead.
How to Get Started with Azure Apps: A Step-by-Step Guide
Starting with Azure apps is easier than you think. Whether you’re a developer, DevOps engineer, or IT manager, this guide will help you deploy your first application.
Setting Up Your Azure Account and Portal Access
The first step is creating a Microsoft Azure account. You can start with a free account that includes $200 in credits and access to over 25 always-free services for 12 months.
- Visit Azure Free Account and sign up with your email.
- Verify your identity and payment method (no charges unless you upgrade).
- Access the Azure portal at portal.azure.com.
Once logged in, you’ll see the dashboard where you can create and manage all Azure resources, including Azure apps.
Creating Your First Web App with Azure App Service
Let’s deploy a simple web app using Azure App Service:
- In the Azure portal, click “Create a resource” and search for “App Service”.
- Click “Create” and fill in the details: subscription, resource group, app name, runtime stack (e.g., .NET, Node.js), and region.
- Choose a pricing tier (start with Free F1 for testing).
- Click “Review + create”, then “Create”.
- Wait a few minutes for deployment to complete.
- Once deployed, click “Go to resource” and browse your app (e.g., https://yourappname.azurewebsites.net).
You now have a live web app. To deploy your code, use Git, GitHub Actions, or FTP. Azure also supports ZIP deploy and Visual Studio integration.
Deploying a Serverless Function with Azure Functions
Next, let’s create a serverless function:
- In the portal, search for “Function App” and click “Create”.
- Enter basic details: function app name, runtime (e.g., Python, JavaScript), version, and region.
- Create a new storage account and Application Insights instance for monitoring.
- Click “Review + create”, then “Create”.
- After deployment, go to the function app and click “Functions” > “Add”.
- Choose a template (e.g., HTTP trigger) and create the function.
- Test it using the built-in console or a tool like Postman.
Your function is now live and can be triggered via HTTP. You can extend it to connect with databases, send emails, or process files.
Advanced Use Cases of Azure Apps in Enterprise Environments
While startups use Azure apps for agility, enterprises leverage them for complex, mission-critical systems.
Microservices Architecture with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Large-scale applications often adopt microservices to improve scalability and maintainability. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a managed Kubernetes offering that integrates tightly with Azure apps.
- Deploy containerized apps using Docker and Kubernetes.
- Scale microservices independently based on demand.
- Use Azure Monitor for containers to track performance.
For example, a banking application might have separate microservices for user authentication, transaction processing, and notifications—all running on AKS and communicating via APIs hosted on Azure API Management.
AKS simplifies cluster management, auto-upgrades, and security patching, allowing teams to focus on code rather than infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud Integration Using Azure Arc
Not all workloads can move to the cloud immediately. Azure Arc extends Azure management to on-premises servers, edge devices, and multi-cloud environments (AWS, GCP).
- Manage Kubernetes clusters across environments from Azure portal.
- Apply consistent policies and security controls.
- Deploy Azure services like App Configuration and Monitor anywhere.
This is crucial for industries with data residency requirements. A government agency can run Azure apps on-premises using Arc while benefiting from Azure’s governance and DevOps tools.
Learn more about Azure Arc here.
Real-Time Data Processing with Azure Stream Analytics
Modern apps often require real-time insights. Azure Stream Analytics integrates with Azure apps to process data from IoT devices, logs, and event hubs in real time.
- Write SQL-like queries to analyze streaming data.
- Output results to Power BI, Azure SQL, or blob storage.
- Trigger alerts or functions based on conditions.
A logistics company could use this to monitor delivery trucks, detect delays, and automatically reroute shipments—enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency.
Best Practices for Optimizing Azure Apps Performance
To get the most out of Azure apps, follow these proven best practices.
Implement CI/CD Pipelines for Faster Deployments
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) are essential for modern development. Azure DevOps and GitHub Actions integrate seamlessly with Azure apps.
- Automate testing and deployment using YAML pipelines.
- Use deployment slots to test changes before going live.
- Enable rollback with slot swapping if issues arise.
This reduces human error, speeds up releases, and improves app reliability.
Monitor and Troubleshoot with Azure Monitor
Proactive monitoring prevents downtime. Azure Monitor collects logs, metrics, and traces from all Azure apps.
- Set up alerts for high CPU, memory, or failed requests.
- Use Application Insights to track user behavior and exceptions.
- Create dashboards for real-time visibility.
For example, if your API suddenly returns 500 errors, Azure Monitor can pinpoint the root cause—whether it’s a database timeout or a memory leak in your code.
Secure Your Apps with Zero Trust Principles
Adopt a zero-trust security model: never trust, always verify.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for Azure portal access.
- Use managed identities instead of hardcoded credentials.
- Restrict network access with NSGs and private endpoints.
Regularly audit access logs and rotate secrets using Azure Key Vault. These steps minimize the risk of breaches and ensure compliance.
Future Trends Shaping the Evolution of Azure Apps
The future of Azure apps is being shaped by AI, edge computing, and low-code platforms.
AI-Powered Development with GitHub Copilot and Azure AI
Microsoft is integrating AI deeply into Azure apps. GitHub Copilot, powered by OpenAI, helps developers write code faster by suggesting entire functions.
- Generate boilerplate code for Azure Functions or Logic Apps.
- Auto-document APIs and workflows.
- Improve code quality with AI-driven suggestions.
Azure AI services like Cognitive Services and Azure Machine Learning can be embedded into apps for image recognition, language processing, and predictive analytics—making apps smarter without deep AI expertise.
Edge Computing and IoT with Azure IoT Edge
As more devices go online, processing data at the edge reduces latency. Azure IoT Edge allows you to run Azure apps on edge devices.
- Deploy Azure Functions or containers to Raspberry Pi or industrial gateways.
- Process sensor data locally before sending to the cloud.
- Reduce bandwidth costs and improve response times.
This is vital for manufacturing, healthcare, and smart cities where real-time decisions are critical.
Low-Code and No-Code Expansion via Power Platform
Microsoft’s Power Platform (Power Apps, Power Automate) is converging with Azure apps. Business users can now build apps without coding, while developers extend them with Azure logic.
- Create custom business apps with Power Apps and connect to Azure SQL.
- Use Power Automate to trigger Azure Functions.
- Embed Power BI dashboards in Azure portals.
This democratizes app development, enabling faster innovation across departments.
What are Azure apps?
Azure apps refer to a suite of cloud-based services from Microsoft Azure that enable developers to build, deploy, and manage applications. These include Azure App Service, Functions, Logic Apps, and more, supporting web, mobile, API, and serverless workloads.
How much does Azure App Service cost?
Azure App Service offers a free tier for basic use. Paid tiers start at around $13/month for the Basic plan, with pricing based on instance size and features. Serverless options like Azure Functions charge per execution, making them cost-effective for low-traffic apps.
Can I use Azure apps for mobile app backends?
Yes, Azure App Service is widely used for mobile backends. It supports REST APIs, authentication via Azure AD or social providers, and push notifications through Azure Notification Hubs—making it ideal for iOS and Android apps.
Is Azure Functions truly serverless?
Absolutely. With Azure Functions, you don’t manage servers. Code runs in response to events, and Azure automatically handles scaling, patching, and infrastructure management. You only pay for the time your code executes.
How do I secure my Azure apps?
Use Azure Active Directory for authentication, Azure Key Vault for secrets, network security groups for traffic control, and enable logging with Azure Monitor. Follow zero-trust principles and regularly audit access permissions.
From startups to global enterprises, Azure apps are redefining how software is built and delivered. With powerful tools for web, serverless, and workflow automation, robust security, and seamless DevOps integration, Azure offers a complete ecosystem for modern application development. As AI, edge computing, and low-code platforms evolve, Azure apps will continue to lead the cloud innovation wave—making it an essential platform for any tech-driven organization.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: