Welcome to the ultimate guide on the Azure Portal—your gateway to Microsoft’s cloud universe. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, mastering this powerful tool is essential for managing cloud resources efficiently and securely.
What Is the Azure Portal?

The Azure Portal is Microsoft’s web-based interface for managing cloud services and resources within the Azure ecosystem. It serves as a centralized dashboard where users can deploy, configure, monitor, and manage virtually every aspect of their cloud infrastructure. Think of it as the control center for your entire Azure environment.
A Unified Management Interface
One of the biggest advantages of the Azure Portal is its unified interface. Instead of juggling multiple tools or command-line interfaces, administrators and developers can access everything—from virtual machines to databases, networking, and AI services—through a single, intuitive platform.
- Access to over 200 Azure services
- Real-time monitoring and alerts
- Role-based access control (RBAC) integration
This consolidation reduces complexity and increases operational efficiency, especially in large-scale deployments.
How It Compares to CLI and PowerShell
While tools like Azure CLI and Azure PowerShell offer powerful scripting capabilities, the Azure Portal excels in visual management and ease of use. For teams that include non-technical stakeholders or those new to cloud computing, the graphical interface lowers the learning curve significantly.
“The Azure Portal is not just a dashboard—it’s a productivity engine for cloud operations.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
However, for automation and repetitive tasks, many professionals combine the portal with CLI scripts or Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or ARM templates.
Navigating the Azure Portal Interface
Once you log in to the Azure Portal, you’re greeted with a clean, customizable dashboard. Understanding its layout is the first step toward mastering cloud management.
Dashboard and Menu Layout
The left-hand navigation menu is your primary access point to all Azure services. From here, you can jump to resources like Virtual Machines, Storage Accounts, App Services, and more. The top bar includes search, notifications, help, and account settings.
- Search bar: Quickly find services or resources
- Notification center: Real-time alerts and updates
- Directory and subscription selector: Switch between tenants and billing accounts
The dashboard itself is fully customizable. You can pin frequently used resources, create multiple dashboards for different teams, and even share them across users.
Customizing Your Dashboard
Customization is one of the most underrated features of the Azure Portal. By tailoring your dashboard, you can prioritize critical metrics and reduce time spent navigating.
To customize, click the ‘Edit’ button on any dashboard. You can then add tiles for specific resources, charts for performance metrics, or even markdown notes for team instructions. For example, a DevOps team might create a dashboard showing CPU usage across VMs, deployment status, and active alerts.
Pro Tip: Use multiple dashboards—one for monitoring, one for cost management, and another for security—to stay organized.
Managing Resources with the Azure Portal
At the heart of the Azure Portal is resource management. Whether you’re deploying a virtual machine or configuring a database, the portal provides a guided, step-by-step experience.
Creating and Deploying Resources
To create a new resource, click the ‘+ Create a resource’ button. This opens the Azure Marketplace, where you can browse services by category—Compute, Networking, AI + Machine Learning, and more.
For instance, launching a Windows Virtual Machine involves selecting the image, choosing a size (like Standard_B2s), configuring networking, setting up authentication, and reviewing costs—all through a visual wizard. Behind the scenes, Azure generates a JSON template that can be reused or automated later.
- Step-by-step deployment wizards
- Estimated cost previews before deployment
- Integration with Azure Policy for compliance
This approach ensures that even complex deployments remain accessible to users without deep coding knowledge.
Organizing Resources with Resource Groups
Resource groups are logical containers that help you organize and manage related resources. For example, all components of a web application—VMs, databases, and load balancers—can be grouped together.
This not only simplifies management but also enables bulk actions like deletion, access control, and cost tracking. When you delete a resource group, all its contained resources are removed, making cleanup efficient and predictable.
Best Practice: Name resource groups clearly (e.g., ‘Prod-WebApp-EastUS’) and apply tags for additional metadata.
Monitoring and Diagnostics in the Azure Portal
Effective cloud management isn’t just about deployment—it’s about visibility. The Azure Portal integrates powerful monitoring tools to help you track performance, troubleshoot issues, and optimize costs.
Using Azure Monitor
Azure Monitor is the central service for collecting, analyzing, and acting on telemetry data from your cloud and on-premises environments. Within the Azure Portal, you can access logs, metrics, and alerts directly from the resource blade.
For example, if a virtual machine is experiencing high CPU usage, you can navigate to its ‘Metrics’ tab, select ‘CPU Percentage’, and view real-time or historical data. You can also set up alerts to notify your team when thresholds are exceeded.
- Custom metric charts
- Log queries using Kusto Query Language (KQL)
- Integration with Application Insights for app performance
Azure Monitor is essential for maintaining uptime and performance, especially in production environments.
Setting Up Alerts and Action Groups
Alerts in the Azure Portal are proactive notifications based on specific conditions. You can configure them for metrics, logs, or activity logs (e.g., when someone deletes a resource).
Action groups define what happens when an alert is triggered—such as sending an email, SMS, calling a webhook, or triggering an Azure Function. This automation ensures rapid response to incidents.
Example: Set an alert when disk usage exceeds 90%, and automatically trigger a script to clean up logs.
These features make the Azure Portal not just a management tool, but a key component of your observability strategy.
Security and Identity Management in the Azure Portal
Security is paramount in cloud environments, and the Azure Portal provides robust tools to manage access, detect threats, and enforce compliance.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC allows you to assign granular permissions to users, groups, and service principals. Instead of giving full access, you can assign roles like ‘Reader’, ‘Contributor’, or custom roles based on the principle of least privilege.
For example, a developer might have ‘Contributor’ access to a dev resource group but only ‘Reader’ access to production. This minimizes the risk of accidental or malicious changes.
- Built-in roles: Owner, Contributor, Reader, User Access Administrator
- Custom roles for specialized permissions
- Scope-based assignments (subscription, resource group, resource)
You can manage RBAC directly from the ‘Access Control (IAM)’ tab in any resource or scope.
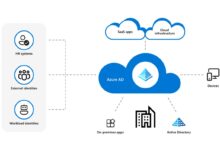
Integrating Azure Active Directory (AAD)
Azure Active Directory is the identity backbone of the Azure Portal. It enables single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and conditional access policies.
When you log in to the Azure Portal, you’re authenticating through AAD. From there, you can manage users, groups, and applications. You can also integrate on-premises Active Directory via Azure AD Connect for hybrid environments.
Security Tip: Always enforce MFA for administrative accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
The integration between AAD and the Azure Portal ensures that identity is not an afterthought—it’s built into every action.
Cost Management and Optimization via Azure Portal
One of the biggest challenges in cloud computing is controlling costs. The Azure Portal provides comprehensive tools to track spending, forecast budgets, and identify savings opportunities.
Using the Cost Management + Billing Service
The Cost Management + Billing section of the Azure Portal gives you full visibility into your spending. You can view daily costs, analyze trends, and break down expenses by resource, service, or tag.
For example, you can see that your Virtual Machines are consuming 60% of your monthly budget, or that a specific department is exceeding its allocated spend. This data is crucial for financial accountability and planning.
- Daily cost reports
- Budget creation with alerts
- Forecasting based on historical usage
You can also export data to CSV or integrate with Power BI for advanced reporting.
Identifying Cost-Saving Opportunities
The Azure Portal doesn’t just show costs—it helps you reduce them. The ‘Recommendations’ tab in the Cost Management section offers actionable insights, such as:
- Downsizing underutilized VMs
- Reserving instances for long-term savings
- Deleting unused disks or public IPs
These recommendations are powered by machine learning and can lead to significant savings—often 20-30% with minimal effort.
Case Study: A mid-sized company reduced its Azure bill by 28% in three months by following portal-generated recommendations.
Automation and DevOps with the Azure Portal
While the Azure Portal is known for its GUI, it also supports advanced automation and DevOps practices, bridging the gap between visual management and code-driven workflows.
Exporting Templates for Infrastructure as Code
Every resource you deploy through the Azure Portal generates an ARM (Azure Resource Manager) template in the background. You can export this template from the resource group blade and reuse it for consistent, repeatable deployments.
This is a powerful way to transition from manual setups to Infrastructure as Code (IaC). Teams can version-control these templates in GitHub, review changes, and deploy via CI/CD pipelines.
- Export templates for audit or backup
- Modify JSON for customization
- Deploy via Azure CLI or DevOps pipelines
This feature makes the Azure Portal a starting point for automation, not just a manual tool.
Integration with Azure DevOps and GitHub
The Azure Portal integrates seamlessly with Azure DevOps and GitHub. You can trigger deployments directly from repositories, monitor pipeline status, and even deploy web apps with a few clicks.
For example, the ‘Deploy to Azure’ button in GitHub repositories opens a deployment wizard in the Azure Portal, pre-filled with configuration options. This lowers the barrier for developers to deploy applications securely and consistently.
DevOps Insight: Use deployment centers in App Services to connect to GitHub, Azure Repos, or Bitbucket for continuous delivery.
Advanced Tips and Best Practices for Azure Portal Mastery
Beyond the basics, there are several advanced techniques that can elevate your efficiency and security when using the Azure Portal.
Leveraging Tags for Resource Organization
Tags are key-value pairs that you can attach to resources for better organization and management. Common uses include:
- Environment (e.g., ‘env:prod’, ‘env:dev’)
- Department (e.g., ‘dept:finance’)
- Cost center or project code
Once tagged, you can filter resources, generate cost reports by tag, and even enforce policies (e.g., ‘All production resources must have an owner tag’).
Tags are invisible to applications but invaluable for operations and finance teams.
Using Azure Policy for Governance
Azure Policy allows you to enforce organizational standards and assess compliance at scale. Through the Azure Portal, you can assign policies that automatically audit or block non-compliant resources.
For example, you can create a policy that ensures all storage accounts are encrypted or that all VMs use managed disks. Policies can be assigned at the subscription or resource group level.
Example Policy: ‘Deny public blob access’ to prevent accidental data leaks.
This proactive governance reduces risk and ensures consistency across your cloud environment.
What is the Azure Portal used for?
The Azure Portal is used to manage Microsoft Azure cloud services through a web-based interface. It allows users to deploy, configure, monitor, and secure resources like virtual machines, databases, and networks—all from a centralized dashboard.
Is the Azure Portal free to use?
Yes, access to the Azure Portal itself is free. However, the resources you create and manage within it (like VMs or storage) incur costs based on usage. You need an Azure account to log in and manage services.
How do I secure access to the Azure Portal?
You can secure access by enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to limit permissions, and applying Conditional Access policies through Azure Active Directory.
Can I automate tasks in the Azure Portal?
Yes, while the portal is GUI-based, it supports automation through features like exporting ARM templates, integrating with Azure DevOps, and using Azure CLI or PowerShell from the portal’s built-in Cloud Shell.
Where can I find cost reports in the Azure Portal?
Cost reports are available under the ‘Cost Management + Billing’ section. You can view detailed spending, set budgets, and get recommendations for savings—all within the Azure Portal interface.
Mastering the Azure Portal is a critical step in harnessing the full power of Microsoft Azure. From intuitive resource management to advanced monitoring, security, and cost control, the portal offers a comprehensive suite of tools for cloud professionals. By leveraging its features—like dashboards, RBAC, cost analysis, and automation—you can build, manage, and optimize cloud environments with confidence. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your skills, the Azure Portal remains an indispensable tool in the modern IT landscape.
Further Reading: