Looking to streamline your data workflows in the cloud? Azure Data Factory might just be the game-changer you need. This powerful ETL service simplifies data integration, enabling seamless movement and transformation across cloud and on-premises sources—without writing a single line of code. Let’s dive into what makes it indispensable.
What Is Azure Data Factory and Why It Matters

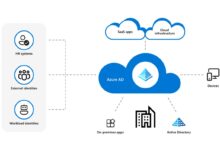
Azure Data Factory (ADF) is Microsoft’s cloud-based data integration service that allows organizations to create data-driven workflows for orchestrating and automating data movement and transformation. Built on a serverless architecture, it enables businesses to ingest, process, and deliver data efficiently across hybrid environments.
Core Definition and Purpose
Azure Data Factory is not just another ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool—it’s a comprehensive data orchestration platform. It enables developers, data engineers, and analysts to construct pipelines that automate the flow of data from diverse sources like SQL Server, Blob Storage, Salesforce, and even on-premises databases into analytics platforms such as Azure Synapse Analytics or Power BI.
- Supports both code-free visual tools and code-based development using JSON or SDKs.
- Enables hybrid data integration across cloud and on-premises systems.
- Integrates natively with other Azure services like Azure Databricks, HDInsight, and Azure Functions.
“Azure Data Factory is the backbone of modern data integration in the Microsoft cloud ecosystem.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
How It Fits into Modern Data Architecture
In today’s data-driven world, organizations deal with massive volumes of structured and unstructured data scattered across multiple platforms. ADF acts as the central nervous system that connects these disparate systems, ensuring timely, accurate, and reliable data delivery for analytics and machine learning.
It plays a critical role in building data lakes, data warehouses, and real-time analytics pipelines. By automating complex workflows, ADF reduces manual intervention, minimizes errors, and accelerates time-to-insight.
For example, a retail company can use ADF to pull daily sales data from point-of-sale systems, combine it with online transaction logs from Azure Cosmos DB, transform it using Azure Databricks, and load it into Azure Synapse for reporting—all scheduled to run every night automatically.
Key Components of Azure Data Factory
To fully harness the power of Azure Data Factory, you need to understand its core building blocks. Each component serves a specific function in the data pipeline lifecycle, from connection to execution.
Linked Services and Data Sources
Linked services are the connectors that define the connection information needed to access external data sources. Think of them as the ‘credentials and endpoints’ that allow ADF to talk to databases, storage accounts, APIs, or even SaaS applications like Dynamics 365.
- Examples include Azure Blob Storage, SQL Database, Oracle, Amazon S3, and REST APIs.
- Supports authentication via keys, service principals, managed identities, and OAuth.
- Enables secure data transfer using private endpoints and virtual networks.
You can configure linked services through the Azure portal, PowerShell, or ARM templates. Once set up, they can be reused across multiple pipelines, promoting consistency and reducing configuration overhead.
Datasets and Data Flows
Datasets represent the structure and location of data within a linked service. They don’t store the actual data but act as pointers or references to where the data resides—like a table in SQL Server or a folder in Blob Storage.
On the other hand, Data Flows are ADF’s visual tool for performing transformations without writing code. Built on Apache Spark, they allow you to clean, aggregate, join, and enrich data using a drag-and-drop interface.
- Datasets support various formats: JSON, CSV, Parquet, Avro, and ORC.
- Data Flows enable scalable transformations with auto-scaling clusters.
- Supports schema drift detection and dynamic column mapping.
For instance, if you’re merging customer data from two different CRMs with slightly different field names, Data Flows can automatically detect and map those fields, saving hours of manual scripting.
Pipelines and Activities
Pipelines are the workflows that define the sequence of operations to be performed on data. Each pipeline contains one or more activities, which are the individual tasks—such as copying data, running a stored procedure, or triggering a Databricks notebook.
- Copy Activity: Moves data between sources and sinks.
- Transformation Activities: Invokes compute services like Azure Databricks or HDInsight.
- Control Activities: Manages workflow logic (e.g., If Condition, ForEach, Wait).
A pipeline can be as simple as copying a file from Blob Storage to a SQL database or as complex as a multi-step ETL process involving data validation, transformation, and notification triggers.
Top 7 Powerful Features of Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory stands out from traditional ETL tools thanks to its rich feature set designed for scalability, flexibility, and ease of use. Here are seven of its most powerful capabilities.
1. Visual Integration and No-Code Development
One of the biggest advantages of ADF is its intuitive, drag-and-drop interface. The Copy Data tool and Data Flow designer allow non-developers to build robust data pipelines without writing SQL or Python.
- Guided wizards simplify source-to-sink mapping.
- Real-time preview of data during transformation.
- Auto-generated scripts for transparency and customization.
This democratizes data integration, allowing business analysts and data stewards to participate in pipeline creation, reducing dependency on IT teams.
2. Built-in Support for Hybrid Data Integration
Many enterprises still rely on on-premises databases like SQL Server or Oracle. ADF handles this seamlessly through the Self-Hosted Integration Runtime (SHIR), which acts as a bridge between cloud and on-premises systems.
- SHIR runs on a local machine or VM and securely communicates with ADF.
- Supports firewall traversal and encrypted data transfer.
- Can be scaled horizontally for high-throughput scenarios.
This makes ADF ideal for organizations undergoing cloud migration while maintaining legacy systems.
3. Serverless Execution and Auto-Scaling
Unlike traditional ETL tools that require dedicated servers, ADF uses a serverless compute model. When you run a pipeline, Azure automatically provisions the necessary resources, scales them based on workload, and shuts them down when done—ensuring cost efficiency.
The Auto-Resolve Integration Runtime dynamically selects the best compute environment, whether it’s a managed Azure environment or a self-hosted node.
“Serverless doesn’t mean no infrastructure—it means you don’t manage it.” — Microsoft Azure Blog
4. Native Integration with Azure Ecosystem
Azure Data Factory isn’t an isolated tool—it’s deeply integrated with the broader Azure data platform. You can easily connect to:
- Azure Databricks for advanced analytics and ML.
- Azure Synapse Analytics for data warehousing.
- Azure Functions for custom logic execution.
- Azure Logic Apps for enterprise workflow automation.
This tight integration reduces complexity and accelerates development.
5. Scheduling and Trigger-Based Workflows
ADF supports multiple ways to trigger pipelines:
- Schedule Triggers: Run pipelines at specific times (e.g., daily at 2 AM).
- Tumbling Window Triggers: Ideal for time-based processing like hourly aggregations.
- Event-Based Triggers: Start a pipeline when a file is uploaded to Blob Storage.
This flexibility allows you to build responsive, event-driven architectures that react instantly to data changes.
6. Monitoring and Management via Azure Monitor
Once pipelines are running, you need visibility. ADF provides a built-in Monitor tab in the Azure portal where you can track pipeline runs, view execution duration, and identify failures.
- View detailed logs and error messages.
- Set up alerts using Azure Monitor and Log Analytics.
- Export metrics to dashboards for real-time oversight.
You can also use PowerShell or REST APIs to automate monitoring tasks.
7. Git Integration and CI/CD Support
For enterprise teams practicing DevOps, ADF offers native Git integration with Azure Repos or GitHub. This enables version control, collaboration, and continuous integration/deployment (CI/CD).
- Develop in a collaboration branch, test, then publish to live.
- Automate deployment using Azure DevOps pipelines.
- Enforce code reviews and approval workflows.
This ensures that data pipelines are treated like software—reliable, testable, and auditable.
How to Get Started with Azure Data Factory
Starting with ADF is straightforward, even if you’re new to cloud data services. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating your first pipeline.
Step 1: Create an ADF Instance
Log in to the Azure portal, navigate to “Create a resource,” search for “Data Factory,” and select it. Choose a name, subscription, resource group, and region. Make sure to select V2, as it’s the latest and most feature-rich version.
Step 2: Launch the Data Factory Studio
After deployment, open the ADF instance and click “Author & Monitor” to launch the web-based development environment. This is where you’ll design pipelines, datasets, and data flows.
Step 3: Build a Simple Copy Pipeline
Click “Create pipeline,” then drag a Copy Data activity onto the canvas. Configure the source (e.g., Blob Storage) and sink (e.g., SQL Database) by creating linked services and datasets. Test the connection, set up scheduling, and publish your pipeline.
Run it manually or wait for the scheduled trigger. Monitor the execution in the Monitor tab.
Common Use Cases for Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory is versatile and can be applied across industries and scenarios. Here are some of the most common use cases.
Data Migration to the Cloud
Organizations moving from on-premises data centers to Azure often use ADF to migrate large volumes of data. Whether it’s SQL databases, flat files, or ERP data, ADF can handle batch and incremental loads efficiently.
- Minimizes downtime during migration.
- Supports delta sync using watermark columns.
- Integrates with Azure Database Migration Service (DMS).
Building Data Lakes and Warehouses
ADF is a key component in constructing modern data architectures. It ingests raw data into Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS), transforms it using Spark-based data flows, and loads it into a data warehouse like Synapse for reporting.
- Enables schema-on-read flexibility.
- Supports ingestion from IoT devices, logs, and social media.
- Facilitates data governance with metadata tagging.
Real-Time Data Processing
With event-based triggers and integration with Azure Event Hubs and Stream Analytics, ADF can support near real-time data processing. For example, a logistics company can process shipment updates as they arrive and update dashboards instantly.
- Triggers pipelines on file arrival or message queue events.
- Combines streaming and batch processing in hybrid pipelines.
- Enables low-latency decision-making.
Best Practices for Optimizing Azure Data Factory
To get the most out of ADF, follow these proven best practices.
Design Modular Pipelines
Instead of creating monolithic pipelines, break them into smaller, reusable components. Use parameters and variables to make pipelines dynamic and adaptable to different environments (dev, test, prod).
- Improve maintainability and reduce duplication.
- Easier to debug and test individual stages.
Leverage Incremental Loading
Avoid full data reloads by implementing incremental (delta) loading. Use watermark columns (e.g., LastModifiedDate) to identify new or updated records since the last run.
This drastically reduces execution time and cost, especially with large datasets.
Monitor Performance and Costs
While ADF is cost-effective, inefficient pipelines can lead to unnecessary spending. Monitor:
- Pipeline execution duration.
- Data movement volume (especially cross-region transfers).
- Integration Runtime usage (SHIR CPU/memory).
Use Azure Cost Management to track ADF expenses and optimize accordingly.
Challenges and Limitations of Azure Data Factory
Despite its strengths, ADF isn’t without limitations. Being aware of these helps in planning better solutions.
Learning Curve for Complex Scenarios
While the visual interface is user-friendly, advanced scenarios involving custom scripts, error handling, or complex control flow require a solid understanding of JSON, expressions, and Azure services.
New users may struggle with debugging failed pipelines or optimizing performance without prior experience.
Cost Management Complexity
ADF pricing is based on pipeline runs, data movement, and data flow execution minutes. Without proper monitoring, costs can spiral—especially with frequent triggers or large transformations.
Tip: Use diagnostic settings and budget alerts in Azure to stay on track.
Dependency on Integration Runtime
For on-premises connectivity, SHIR is essential but introduces operational overhead. It must be installed, maintained, and scaled manually. Network latency and firewall rules can also impact performance.
Consider using Azure ExpressRoute for high-speed, secure connections.
Future Trends and Innovations in Azure Data Factory
Microsoft continues to enhance ADF with new features and integrations. Here’s what’s on the horizon.
AI-Powered Data Mapping
Microsoft is exploring AI-driven suggestions for field mapping and transformation logic. Imagine ADF automatically recommending how to map “cust_id” to “customer_id” based on historical patterns.
This could reduce setup time and improve accuracy in data integration.
Enhanced Real-Time Capabilities
Future updates may include tighter integration with Azure Stream Analytics and Event Grid, enabling true real-time orchestration—not just near real-time.
This would open doors for use cases in fraud detection, predictive maintenance, and live customer analytics.
Low-Code Expansion
Microsoft is investing heavily in low-code platforms. Expect ADF to offer even more drag-and-drop capabilities, pre-built templates, and natural language interfaces for pipeline creation.
Soon, you might be able to say, “Create a pipeline that copies yesterday’s sales data to Synapse,” and ADF will generate it automatically.
What is Azure Data Factory used for?
Azure Data Factory is used for orchestrating and automating data movement and transformation across cloud and on-premises sources. It’s commonly used for ETL processes, data migration, building data lakes, and enabling analytics and machine learning workflows.
Is Azure Data Factory a ETL tool?
Yes, Azure Data Factory is a cloud-based ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and data integration service. It allows users to create pipelines that extract data from various sources, transform it using tools like Data Flows or Azure Databricks, and load it into destination systems for analysis.
How much does Azure Data Factory cost?
Azure Data Factory has a consumption-based pricing model. The basic tier is free up to a certain number of pipeline runs. Beyond that, you pay for pipeline activities, data movement, and data flow execution minutes. Costs vary based on usage, region, and integration runtime type. Detailed pricing is available on the official Azure pricing page.
Can Azure Data Factory replace SSIS?
Yes, Azure Data Factory can replace SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) in many scenarios, especially for cloud and hybrid workloads. Microsoft provides the SSIS Integration Runtime within ADF to migrate existing SSIS packages to the cloud without rewriting them.
How does Azure Data Factory integrate with other Azure services?
Azure Data Factory integrates natively with services like Azure Blob Storage, Azure SQL Database, Azure Databricks, Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Functions, and Logic Apps. This deep integration allows seamless data flow across the Azure ecosystem, enabling end-to-end data solutions.
Azure Data Factory is more than just a data integration tool—it’s a powerful orchestration engine that empowers organizations to build scalable, reliable, and automated data pipelines. From simple file transfers to complex hybrid ETL workflows, ADF provides the flexibility and performance needed in today’s data landscape. Whether you’re migrating to the cloud, building a data lake, or enabling real-time analytics, Azure Data Factory offers the tools and ecosystem to succeed. As Microsoft continues to innovate, ADF is set to become even more intelligent, accessible, and integral to modern data strategies.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: